
This research projects aims to accelerate the recovery process of patients that have suffered COVID and have neuromotor sequelae that hamper their hand movility as a consequence, preventing them to carry out daily life activities. The technical objective of this project is to design and develop specific therapies to treat COVID-caused neuromotor problems, as well as the redesign and readaptation of the ROBHAND robot for this kind of patients.
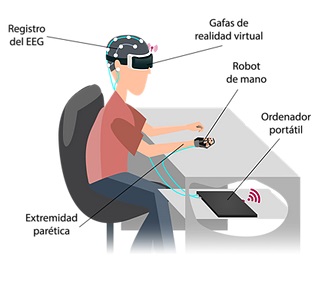
In this innovative experimental development project, a neurorehabilitation platform will be developed (M3Rob - Mind - Hand - Robot Wrist), that will allow the realization of new therapies to address, simultaneously, the rehabilitation of cognitive and neuromotor functions, for patients who have suffered a stroke. With this platform, patients will be able to perform therapies oriented to activities of daily living for neuromotor rehabilitation, and it will also allow training / rehabilitating the higher cognitive functions affected by their injury. This approach to neuromotor and cognitive rehabilitation will improve the patient’s rehabilitation and benefit from the combined effects of both therapeutic approaches.
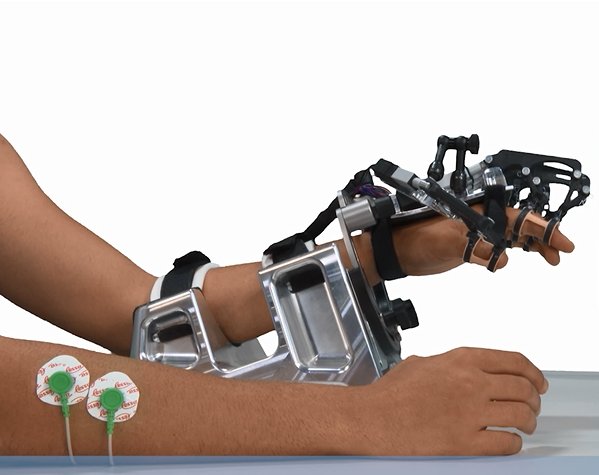
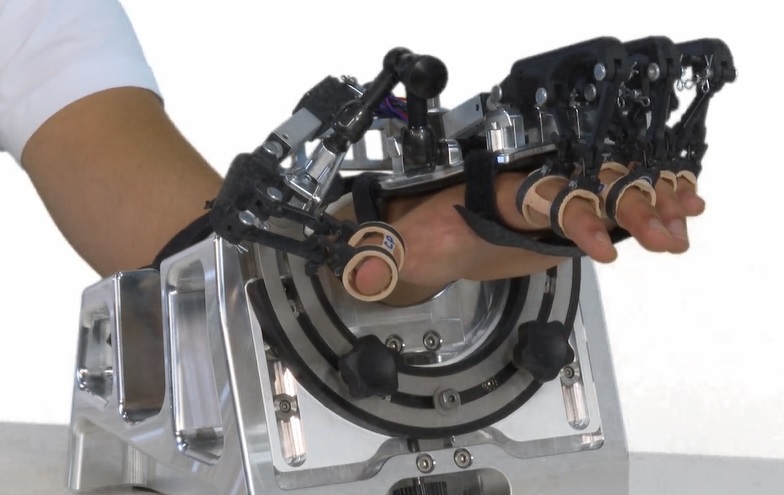
This project aims to develop RobHand robot, a new robot for hand rehabilitation, through active therapies, for patients who have neuromotor disability due to a Vascular Brain Accident. It is an exoskeleton type robot, conceived to provide active therapies related to the rehabilitation of hand grip and pronation / supination of the forearm. This robotic device will allow the development of adequate motor control to achieve a “fine” manipulation of the objects, adapted to the different grip strategies that each patient can implement. The aim of this new design is to provide a more complete rehabilitation platform, adaptable to patients with a greater number of deficiencies thanks to an improvement in several areas: improvement in the mechanical structure, making it “transparent”, improving control haptic to provide assistance tailored to the needs of the patient, improving the design and implementation of virtual environments for therapies, so that they are motivating and friendly.
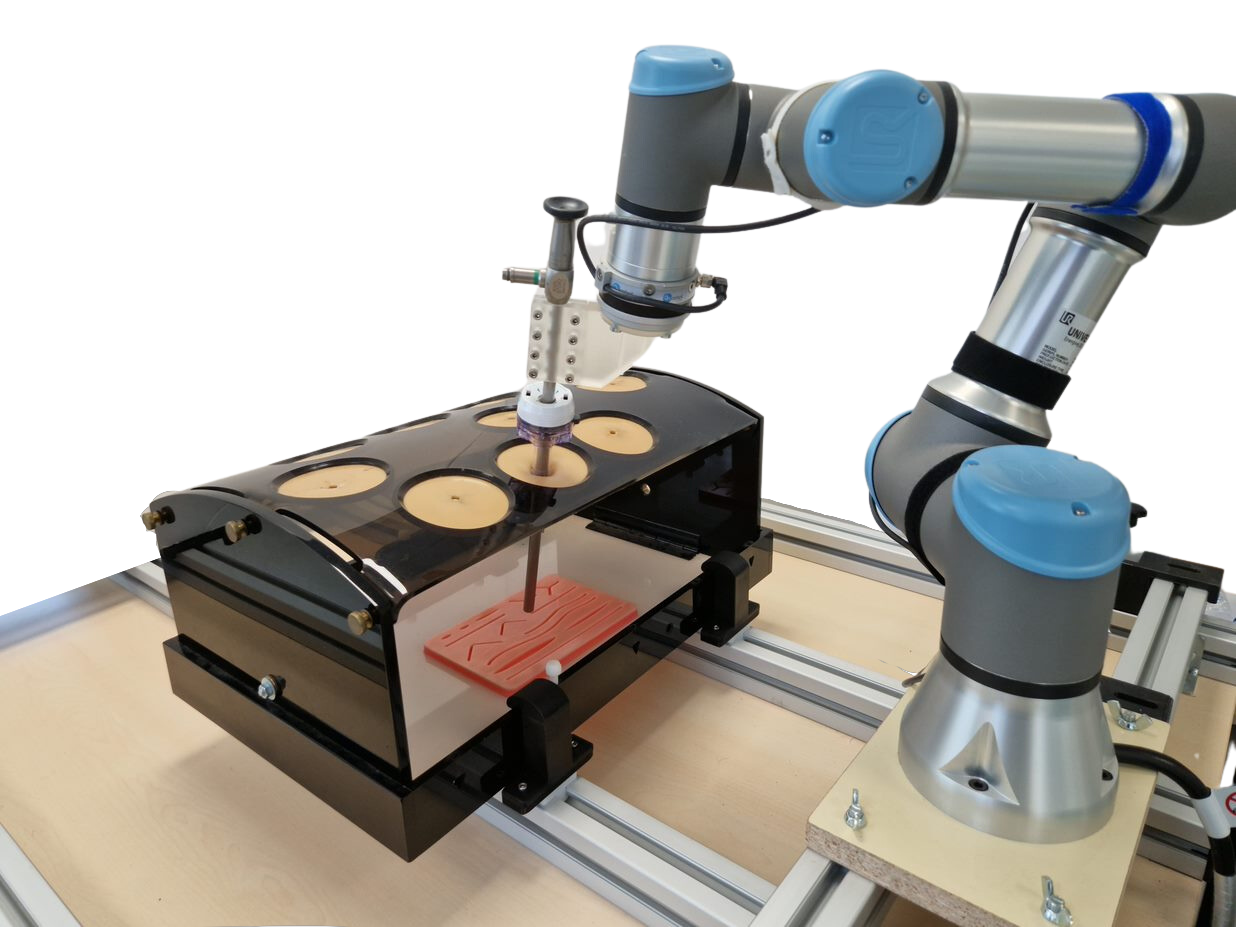
The general objective of this project focuses on the development of technologies for providing a robotic assistant for laparoscopic liver surgery with skills for helping in the resolution of bleeding events that occur during surgery, as well as the management of both an intraoperative ultrasound probe and the endoscope. All these functionalities will be integrated and validated under a cognitive scheme.
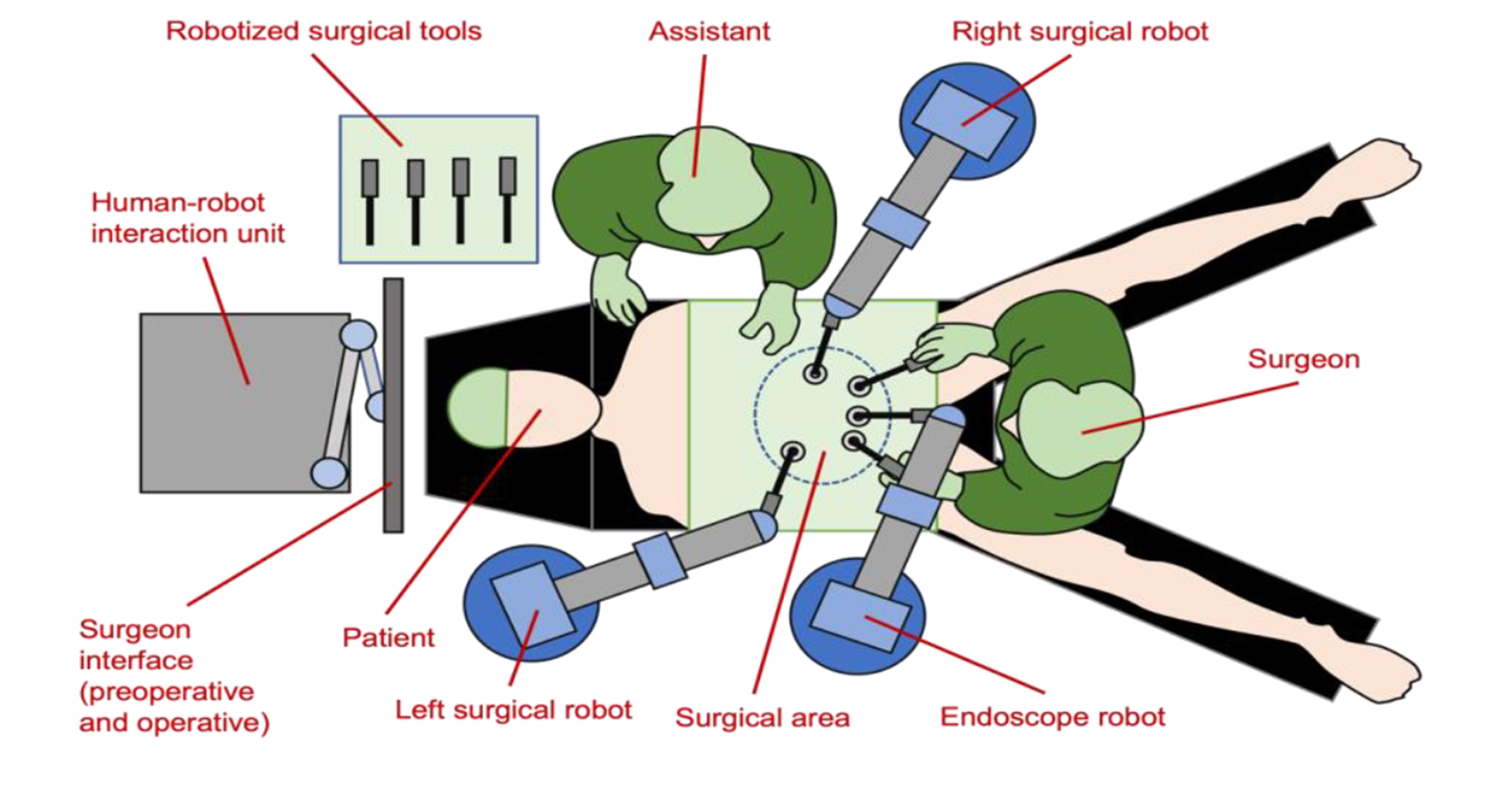
This research project proposes a leap from the current conception of robotic laparoscopic surgery, focused on tele-operated robots. It proposes a co-worker robot within the concept of surgery 4.0 able to assist the surgeon in procedures of laparoscopic sutures. The robotic system will be composed by five arms: a cameraman robot, two tele-operated arms with haptics capabilities, and two autonomous robotic arms. This assistance will be developed thanks to fault-tolerant cognitive architecture with intervention supervision, which uses a qualitative representation of the workflow in order to plan the actuations to assist to the surgeon. These actuations will be executed by a fault tolerance motion control able to coordinate the different arm movements.
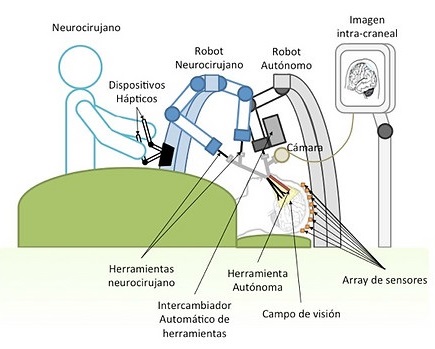
The project that is being developed studies the extension of the concept of robotic system “co-worker”, within a cognitive learning scheme, applied to the endonasal approach. It will provide the neurosurgeon with safety in the intervention through assistance in the form of automatic, collaborative, or shared control movements, as well as with augmented reality. The robotic system will adapt to the ergonomics of the intervention, perform a precise surgical navigation, based on the online information provided to measure the brain-shift effect and take into account the pre-operative planning. Also, it will have an automatic exchanger of surgical tools. In this way, the robotic system will incorporate within a fault tolerant cognitive architecture, a movement control system that avoids damage to the nasal passages, a collaborative movement planner with learning capacity and a mathematical model for the prediction of three-dimensional displacements. of the brain based on intra-operative information.
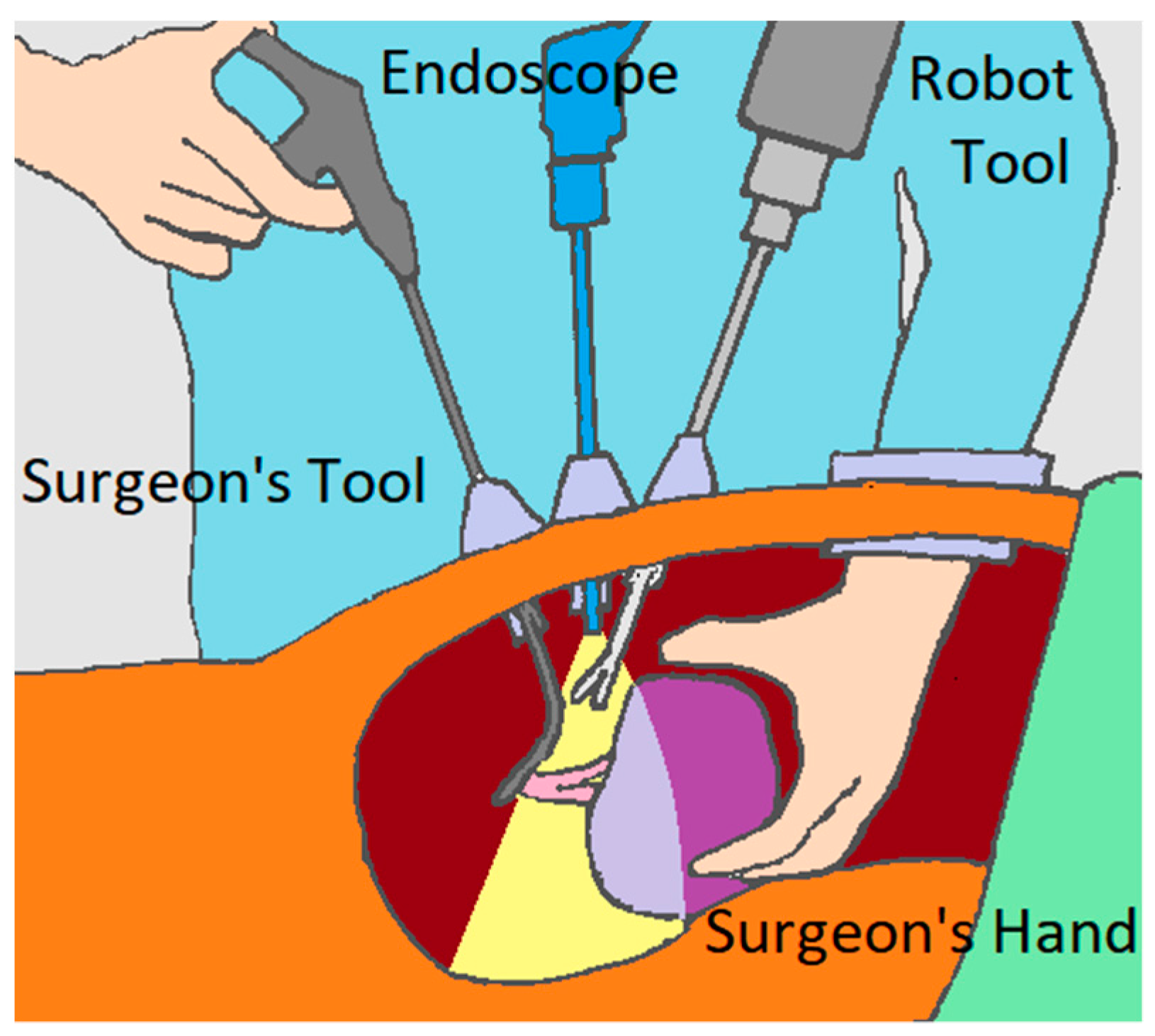
The developed project addressed the development of a robotic system oriented to the HALS approach and framed within the “co-worker” robot concept, where the machine works side by side with the surgeon, collaborating in the surgical maneuvers and learning from the practice. For this, the robotic system that is proposed is formed by a manipulator capable of operating an articulated laparoscopic tool and an endoscope, and another specialized in the movement of mini-robots within the abdominal cavity. On the other hand, it includes a person-machine interface based on an intelligent surgical glove and the ability to emulate the concept of “transparent abdomen” by combining real image with augmented reality.
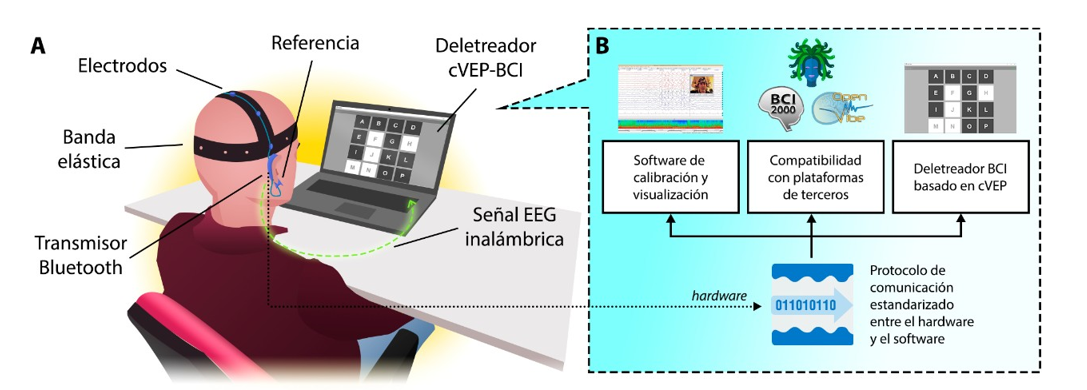
The general objective of the project is to develop new electroencephalography (EEG) recording technology, both in terms of hardware and software, in order to democratize the use and enhance the performance of assistive Brain-Computer Interface (BCI) systems through the development of deep learning techniques. This requires the design, development, and validation of both the hardware and software of the proposed system, enabling the creation of a portable and versatile device capable of capturing a sufficiently high-quality signal to control assistive BCIs, at a lower cost than the existing clinical EEG technology available in the market.
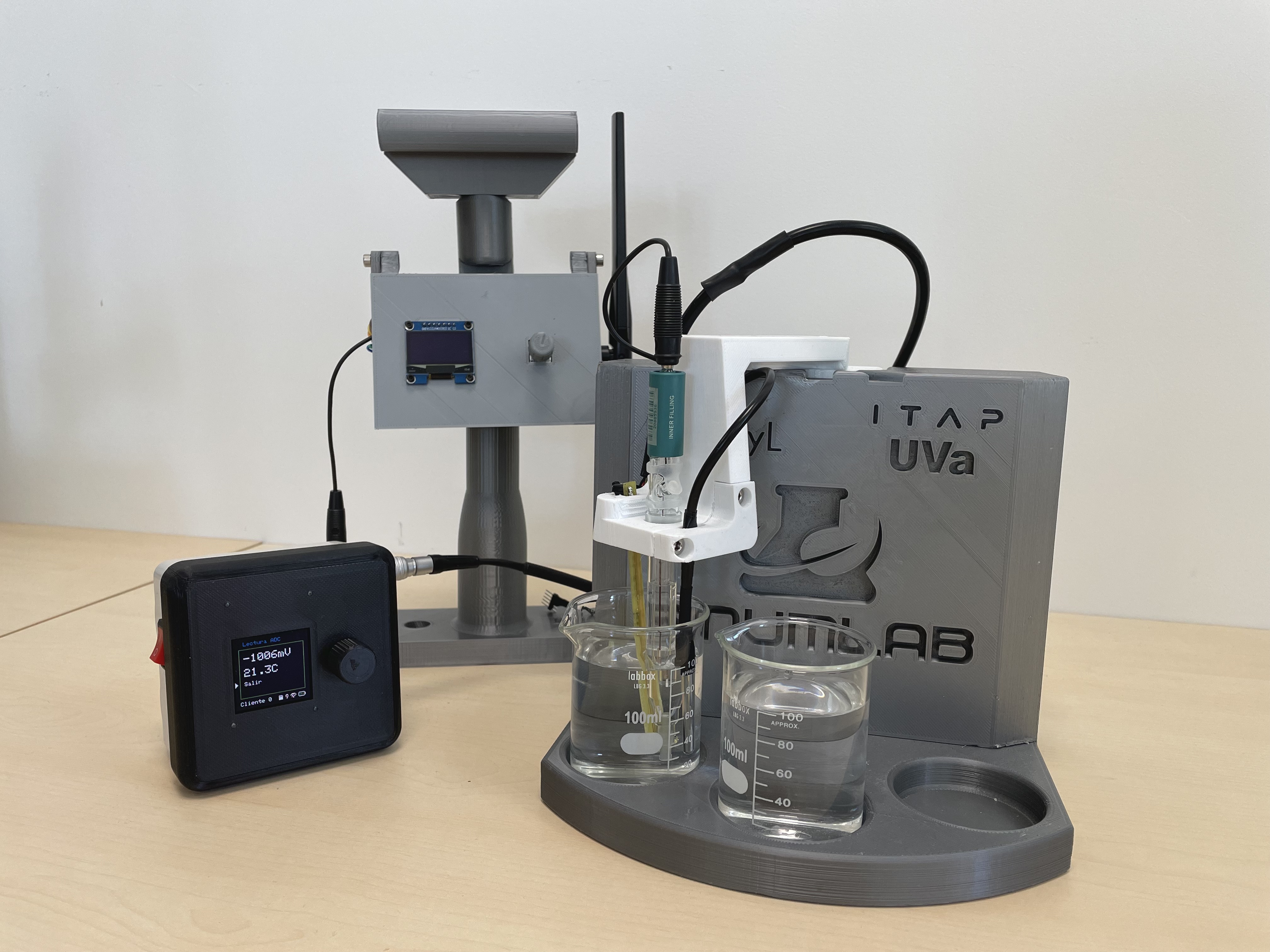

The main objective of this project is to research and design a novel electronic device that leverages ISFET sensor to study variables and chemical characteristics of a substance that need to be analyzed without the need of a laboratory analysis. When applied to the agri-food sector, this device will allow the optimization of fertilization or water and crops treatment processes utilizing the gathered real time knowledge of the previously mentioned variables. A scientifically validated chemical variable measurement device will be designed and built with the purpose of speeding up the analysis work, facilitate portability from the laboratory to the field, reduce analysis costs and allow results to be known in real time, to be a benchmark in the field of chemical analysis using contact sensors in real time.

The general objective of this project is the creation, development and implementation in the cattle sector of the extensive beef, of a new animal management and management system that allows knowledge and improvement of the health status of the animals (through monitoring not invasive of physical and animal variables heart rate, temperature, respiration), and allow work to improve the fertility and prolificacy rates of the livestock, optimize the management and control of livestock, and improve economic efficiency of livestock farms through control and cost savings.
We are part of the ITAP (Institute of Advanced Production Technologies) at the School of Industrial Engineering, University of Valladolid.
© 2024 ITAP Medical Robotics Group.
Site made with Jekyll
Copy and modify it for your own research group.